Remote Sensing and Machine Learning based Optimization of Erosion in Ghizer District-Hindukush Using RUSLE and Hypsometric Modeling
Keywords:
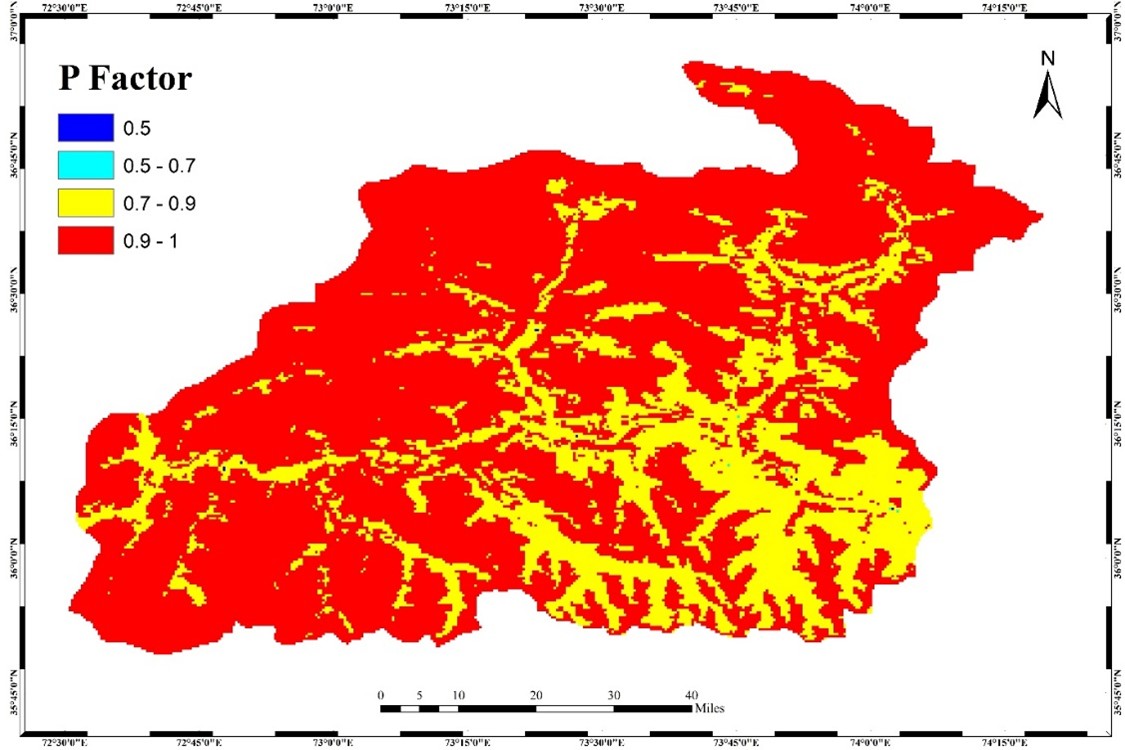
RUSLE, RS, ML, R factor, K factor, LS factor, C factor, P factor, HI.Abstract
Soil erosion-induced land degradation is now considered one of the most severe challenges of the 21st century, with acute risks to soil fertility, food security, human well-being, and global ecosystems. The objective of this study is to conduct a quantitative mapping of soil loss within the Ghizer district of Pakistan. To estimate soil loss in the region, the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model was employed in conjunction with Remote Sensing (RS) and Geographic Information System (GIS) techniques. Analysis of the topographical characteristics of the study area reveals heightened vulnerability to soil loss, with the highest average annual soil loss recorded at 74 tons per hectare per year. The generated maps illustrate that the area exhibits the highest sediment yield of 246 tons per hectare per year, with an elevated average annual soil loss of 435 tons per year. The distribution across severity classes indicates 7% under the very high category, 14% under high, 18% under moderate, 10% under low, and 12% under very low soil loss categories within the Ghizer district. The results of this research help develop a rich information source for researchers and planners to develop more effective approaches for reducing soil loss within high-severity zone categories. Recommendations include the implementation of tree plantation initiatives and the construction of structures such as check dams, which have demonstrated effectiveness in controlling the process of soil erosion. Hypsometric Integrals (HIs) are estimated from empirical formulae based on the geographical plots of the measured contour elevation and the area they encompass. This study aims to calculate hypsometric integral values for the Ghizer River and its sub-watersheds in Hindukush using four different techniques and to compare the procedural techniques of its estimation and relevance to the erosion status. The hypsometric integral expresses precisely the ratio of relief elevation; it is not so cumbersome to use and can be computed easily within an RS environment.