Spatio-Temporal Traffic Congestion Analysis Using AI-Driven Modeling Near Industrial Zones: A Case Study of LIMAK Cement Factory, North Karachi
Keywords:
Industrial Zones, Traffic Congestion, Spatio-Temporal Patterns, GIS, AI-driven Forecasting, Heavy VehiclesAbstract
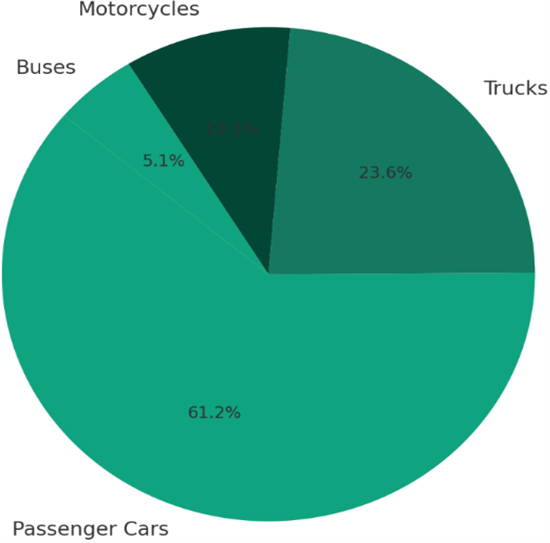
Industrial zones are often the epicenters of intense vehicular movement, contributing significantly to urban traffic congestion and inefficiencies in mobility planning. This study investigates the spatio-temporal traffic patterns near the LIMAK Cement Factory in North Karachi by integrating geographic information system (GIS) techniques with artificial intelligence (AI)-driven forecasting methods. Using publicly available and simulated data, hourly traffic volume, vehicle type distribution, and congestion queue lengths were analyzed to identify hotspots and peak congestion periods. The results highlight significant congestion near Roundabout E89 and Overpass C, with a high proportion of heavy vehicles contributing to delays, particularly during morning and evening rush hours. These findings are consistent with recent research advocating for the deployment of spatio-temporal deep learning models such as ST-GCNs and Transformer-based architectures to manage urban traffic dynamics more effectively. The discussion suggests future directions involving adaptive signal control, transfer learning for data-scarce environments, and decentralized traffic management systems. This study emphasizes the urgent need to adopt intelligent traffic control solutions tailored for industrial corridors in developing urban areas.