Spatiotemporal Data Fusion Using Computational Intelligence for High-Resolution Urban Environmental Monitoring
Keywords:
CNN-LSTM, Satellite Imagery, Predictive AccuracyAbstract
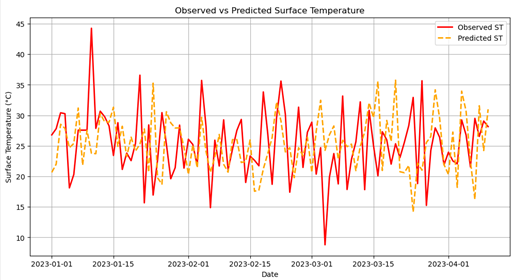
Rapid urbanization and environmental degradation present significant challenges for sustainable urban management. Accurate, high-resolution monitoring of environmental parameters is essential for informed decision-making in smart cities. This study proposes a computational intelligence-based spatiotemporal data fusion framework to integrate heterogeneous datasets, including satellite imagery, ground-based sensors, and social media data, for urban environmental monitoring. The framework employs deep learning models, specifically CNN-LSTM architectures, combined with spatial semantics and knowledge mapping to enhance temporal continuity, spatial resolution, and predictive accuracy of key environmental indicators such as NDVI, surface temperature, and PM₂.₅ concentrations. Quantitative evaluation demonstrates strong agreement between observed and predicted values, with R² exceeding 0.88 for all parameters, highlighting the robustness of the approach. Seasonal patterns in vegetation and temperature, as well as spatial hotspots in air pollution, were effectively captured, supporting decision-making for urban planning, digital twin construction, and sustainable governance. The study confirms that multi-source data fusion, coupled with computational intelligence, can provide high-resolution, actionable insights for urban environmental management. Future work should focus on real-time data integration, scaling to regional levels, and enhancing predictive capabilities for complex urban systems.