Enhancing Fragmentary Spatial–Temporal Reasoning through Hybrid Qualitative Calculi: An Integrated Approach for Robust Inference under Incomplete Observations
Keywords:
Spatial–Temporal Reasoning, Fragmentary Observations, Region Connection Calculus (RCC8), Allen’s Interval AlgebraAbstract
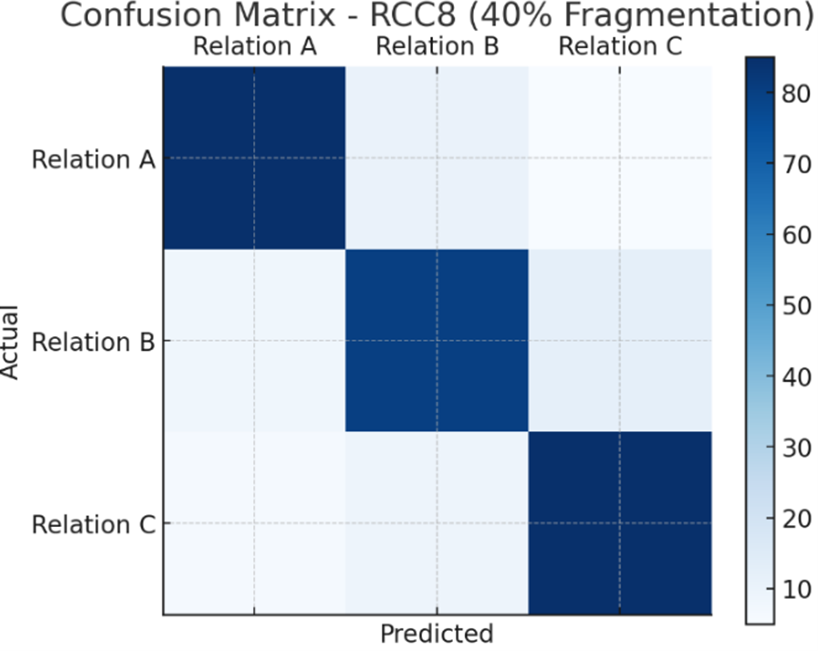
Fragmentary observations of spatial and temporal phenomena pose a significant challenge in fields such as GIS, autonomous navigation, and cognitive robotics, where comprehensive data is often unavailable. This study investigates an integrated approach to spatial–temporal reasoning under incomplete data conditions by combining fragmentary representations with hybrid qualitative reasoning calculi. We model spatial relations using Region Connection Calculus (RCC8) and temporal dependencies using Allen’s Interval Algebra, and subsequently integrate these through a hybrid reasoning framework that supports contextual inference and cross-domain relational mapping. Using both publicly available and synthetically generated datasets, we evaluate the performance of individual calculi and the proposed hybrid model under various fragmentation levels (20%, 40%, 60%). Results show that the hybrid model significantly improves reasoning accuracy, particularly in highly fragmented scenarios, with marked reductions in relational confusion and misclassification. Our findings confirm that hybrid reasoning systems offer enhanced robustness and interpretability, making them suitable for real-time and uncertain environments. This work contributes to the development of intelligent systems capable of dynamic decision-making under data sparsity, and paves the way for future research in hybrid reasoning architectures.