Digital Twins as the Predictive Core of Smart Cities: A Systematic Review and Conceptual Framework for Sustainable Urban Futures
Keywords:
Urbanization, Digital Twin (DT), Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML)Abstract
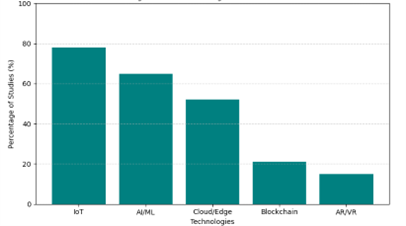
Urbanization is accelerating at an unprecedented pace, creating complex challenges related to infrastructure, mobility, healthcare, energy, and environmental sustainability. Digital Twin (DT) technology has emerged as a transformative tool within smart cities, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and data-driven decision-making through the integration of IoT, AI, ML, blockchain, and cloud/edge computing. This study conducts a systematic review of 148 peer-reviewed publications from 2014 to 2023, alongside an analysis of prominent global case studies, to evaluate the current state, technological enablers, application domains, and challenges of DT adoption in smart cities. Results reveal a steep increase in DT-related research after 2017, with Europe and Asia leading global contributions. Urban planning, transportation, and energy management dominate existing applications, while healthcare and environmental monitoring represent emerging domains. Key technological enablers include IoT and AI/ML, whereas challenges such as interoperability, data governance, scalability, and inclusivity hinder large-scale implementation. Building on these findings, the study proposes a five-layer conceptual framework positioning DTs as the predictive and integrative core of future smart cities, comprising data, processing, simulation, application, and governance layers. The framework emphasizes not only technological integration but also ethical and regulatory considerations to ensure equitable urban development. This research contributes to advancing theoretical and practical understanding of DT-enabled smart cities and highlights pathways for achieving sustainable, resilient, and citizen-centered urban futures.