Bioactive Properties and Nutritional Value of Camel Milk: An Updated Overview
Keywords:
Camel Milk, Nutritional Content, Biological Structure, Therapeutic BenefitsAbstract
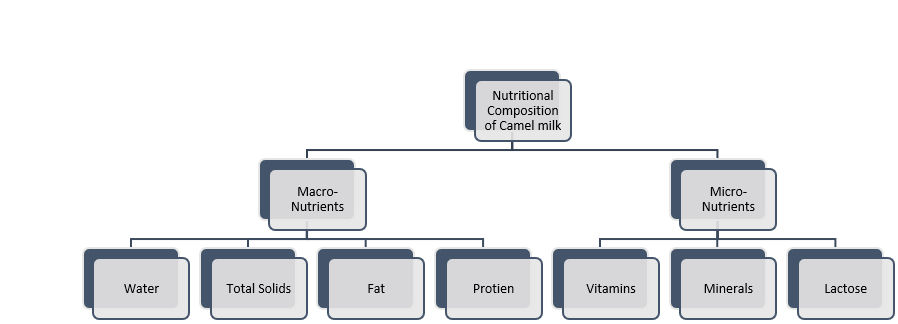
Traditionally sipped in dry areas, camel milk has been of interest from all around the world because of its unusual nutritional makeup and possible therapeutic benefits. This paper provides an overview of the dietary components as well as the health advantages linked to consuming camel milk. Protein, vitamins (especially the B and C vitamins), minerals (calcium, potassium, and magnesium), and important fatty acids are all abundant in camel milk. Moreover, it has bioactive substances that support its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory qualities, including lysozyme, lactoferrin, and immunoglobulin. Research indicates that camel milk might provide medical benefits for many illnesses, such as autism spectrum disorder, diabetes, heart disease, and gastrointestinal issues. Additionally, camel milk has been investigated as a potential replacement for milk from cows in cases of lactose intolerance or allergy to milk proteins. To completely evaluate its therapeutic potential and understand the processes underlying its health advantages, more research is necessary. All things considered, camel milk shows potential as a functional food with a variety of nutritional and therapeutic qualities, offering hope for both therapeutic and preventive uses in human health.