Digital Authoritarianism in Hybrid Regimes: Comparative Insights from Turkey, Hungary, and India
Keywords:
Digital Authoritarianism, Hybrid Regimes, Turkey, Hungary, India, Civic Engagement, Authoritarian ControlAbstract
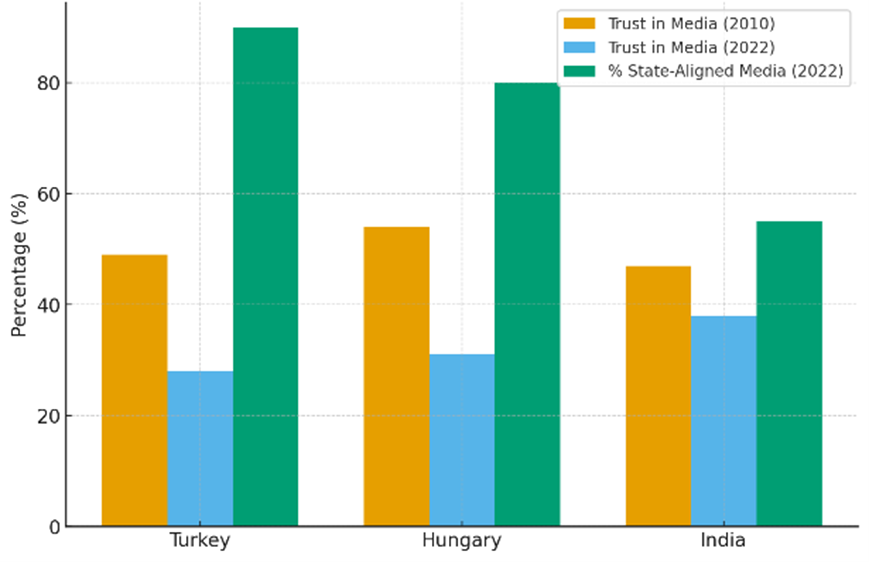
The rapid proliferation of digital technologies has reshaped the global political landscape, offering both avenues for civic engagement and tools for authoritarian control. This study examines the dynamics of digital authoritarianism in hybrid regimes, focusing on Turkey, Hungary, and India, where democratic institutions coexist with pervasive authoritarian practices. Employing a qualitative comparative framework, the research integrates case study analysis, thematic coding, and discourse analysis of legal documents, policy reports, and media content. Findings reveal three convergent mechanisms underpinning digital repression: legal weaponization, securitization of dissent, and media capture. While Turkey relies on overt censorship and prosecutions, Hungary emphasizes covert surveillance and media consolidation, and India exhibits extensive internet shutdowns coupled with biometric monitoring. Quantitative indicators, including Freedom on the Net scores, internet shutdown data, and media-trust metrics, demonstrate significant erosion of democratic freedoms and civic engagement between 2018 and 2022. The study underscores the socio-psychological and economic consequences of digital authoritarianism and highlights the strategies through which hybrid regimes maintain electoral legitimacy while systematically undermining democracy. These insights contribute to theoretical and policy debates on authoritarian resilience in digitally mediated political systems.